Connecting the Dots between Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review
Main Article Content
Abstract
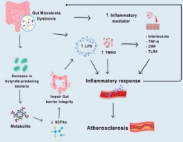
The prevalence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) is rising despite improvements in risk factor management. Numerous causes, including lifestyle modifications, environmental conditions, and gut microbiota dysbiosis, could be blamed for this. The type of bacteria involved and their primary role in atherosclerosis remain unknown even though the association between gut microbiota and atherosclerosis has been explored. Through a systematic review, this study sought to understand how dysbiosis of the gut microbiota contributes to atherosclerosis. PubMed, EBSCOhost, EMBASE, and Cochrane were searched for relevant literature. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for nonrandomized studies was used to measure the risk of bias, and study selection was conducted following PRISMA 2020 recommendations. Both subclinical and symptomatic atherosclerosis were taken into account. Seven of the 783 studies that included 566 patients with vascular disease associated with atherosclerosis met the inclusion criteria. The composition of the gut microbiota varied considerably between the healthy control group and the atherosclerotic group. Patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) have lower alpha diversity. Atherosclerosis was linked to an increase in potentially hazardous bacteria such as Escherichia sp., Shigella sp., Enterococcus sp., and Ruminococcus gnavus and a decrease in helpful bacteria like Subdoligranulum, Roseburia, Faecalibacterium, and Eubacterium rectale. Conclusively, changes in the makeup of the gut microbiota shown in the atherosclerotic group might have caused an imbalance in the synthesis of metabolites, indicating that dysbiosis of the gut microbiota may contribute to cardiovascular disease in several ways.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
Bauersachs R, Zeymer U, Brière JB, Marre C, Bowrin K, Huelsebeck M. Burden of Coronary Artery Disease and Peripheral Artery Disease: A Literature Review. Cardiovasc Ther. 2019;8295054
Al Samarraie A, Pichette M, Rousseau G. Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Development of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5420.
Mansuri NM, Mann NK, Rizwan S, Mohamed AE, Elshafey AE, Khadka A, Mosuka EM, Thilakarathne KN, Mohammed L. Role of Gut Microbiome in Cardiovascular Events: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2022;14(12):e32465.
Witkowski M, Weeks TL, Hazen SL. Gut Microbiota and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Res. 2020;127(4):553-570.
Belli M, Barone L, Longo S, Prandi FR, Lecis D, Mollace R, Margonato D, Muscoli S, Sergi D, Federici M, Barillà F. Gut Microbiota Composition and Cardiovascular Disease: A Potential New Therapeutic Target?. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(15):11971.
Choroszy M, Litwinowicz K, Bednarz R, Roleder T, Lerman A, Toya T, Kamiński K, Sawicka-Śmiarowska E, Niemira M, Sobieszczańska B. Human Gut Microbiota in Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Metabolites. 2022;12(12):1165.
Lancellotti P. Acute and chronic coronary artery disease. Acta Cardiol. 2024;79(2):105-108.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R, Glanville J, Grimshaw JM, Hróbjartsson A, Lalu MM, Li T, Loder EW, Mayo-Wilson E, McDonald S, McGuinness LA, Stewart LA, Thomas J, Tricco AC, Welch VA, Whiting P, Moher D. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
Zhu Q, Gao R, Zhang Y, Pan D, Zhu Y, Zhang X, Yang R, Jiang R, Xu Y, Qin H. Dysbiosis signatures of gut microbiota in coronary artery disease. Physiol Genomics. 2018;50(10):893-903.
Jie Z, Xia H, Zhong SL, Feng Q, Li S, Liang S, Zhong H, Liu Z, Gao Y, Zhao H, Zhang D, Su Z, Fang Z, Lan Z, Li J, Xiao L, Li J, Li R, Li X, Li F, Ren H, Huang Y, Peng Y, Li G, Wen B, Dong B, Chen JY, Geng QS, Zhang ZW, Yang H, Wang J, Wang J, Zhang X, Madsen L, Brix S, Ning G, Xu X, Liu X, Hou Y, Jia H, He K, Kristiansen K. The gut microbiome in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):845.
Baragetti A, Severgnini M, Olmastroni E, Dioguardi CC, Mattavelli E, Angius A, Rotta L, Cibella J, Caredda G, Consolandi C, Grigore L, Pellegatta F, Giavarini F, Caruso D, Norata GD, Catapano AL, Peano C. Gut Microbiota Functional Dysbiosis Relates to Individual Diet in Subclinical Carotid Atherosclerosis. Nutrients. 2021;13(2):304.
Toya T, Corban MT, Marrietta E, Horwath IE, Lerman LO, Murray JA, Lerman A. Coronary artery disease is associated with an altered gut microbiome composition. PLoS One. 2020;15(1):e0227147.
Szabo H, Hernyes A, Piroska M, Ligeti B, Fussy P, Zoldi L, Galyasz S, Makra N, Szabo D, Tarnoki AD, Tarnoki DL. Association between Gut Microbial Diversity and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(3):195.
Yoshida N, Emoto T, Yamashita T, Watanabe H, Hayashi T, Tabata T, Hoshi N, Hatano N, Ozawa G, Sasaki N, Mizoguchi T, Amin HZ, Hirota Y, Ogawa W, Yamada T, Hirata KI. Bacteroides vulgatus and Bacteroides dorei Reduce Gut Microbial Lipopolysaccharide Production and Inhibit Atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2018;138(22):2486-2498.
Cui L, Zhao T, Hu H, Zhang W, Hua X. Association Study of Gut Flora in Coronary Heart Disease through High-Throughput Sequencing. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:3796359.
Rowland I, Gibson G, Heinken A, Scott K, Swann J, Thiele I, Tuohy K. Gut microbiota functions: metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur J Nutr. 2018;57(1):1-24.
Otsu Y, Ae R, Kuwabara M. Folate and cardiovascular disease. Hypertens Res. 2023;46(7):1816-1818.
Brix S, Eriksen C, Larsen JM, Bisgaard H. Metagenomic heterogeneity explains dual immune effects of endotoxins. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135(1):277-280.
Zhu J, Lyu J, Zhao R, Liu G, Wang S. Gut macrobiotic and its metabolic pathways modulate cardiovascular disease. Front Microbiol. 2023;14:1272479.
Tassoni DS, Macedo RCO, Delpino FM, Santos HO. Gut Microbiota and Obesity: The Chicken or the Egg? Obesities. 2023; 3(4):296-321.
Mao Y, Kong C, Zang T, You L, Wang LS, Shen L, Ge JB. Impact of the gut microbiome on atherosclerosis. mLife. 2024;3(2):167-175.
Shen X, Li L, Sun Z, Zang G, Zhang L, Shao C, Wang Z. Gut Microbiota and Atherosclerosis-Focusing on the Plaque Stability. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:668532.
Drosos I, Tavridou A, Kolios G. New aspects on the metabolic role of intestinal microbiota in the development of atherosclerosis. Metabolism. 2015;64(4):476-481.
Zhu W, Gregory JC, Org E, Buffa JA, Gupta N, Wang Z, Li L, Fu X, Wu Y, Mehrabian M, Sartor RB, McIntyre TM, Silverstein RL, Tang WHW, DiDonato JA, Brown JM, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL. Gut Microbial Metabolite TMAO Enhances Platelet Hyperreactivity and Thrombosis Risk. Cell. 2016;165(1):111-124.
Crovesy L, Masterson D, Rosado EL. Profile of the gut microbiota of adults with obesity: a systematic review. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2020;74(9):1251-1262.
Ziganshina EE, Sharifullina DM, Lozhkin AP, Khayrullin RN, Ignatyev IM, Ziganshin AM. Bacterial Communities Associated with Atherosclerotic Plaques from Russian Individuals with Atherosclerosis. PLoS One. 2016;11(10):e0164836.
Hanson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(16):1685-1695.