Amelioration of Paraquat-Induced Hippocampal Damage and Cognitive Impairment by Selenium and Magnesium in Mice
Main Article Content
Abstract
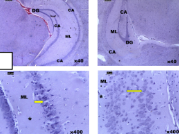
Paraquat (Pq) is an extremely toxic herbicide that causes oxidative stress by generating superoxide anions, leading to cellular damage and cognitive impairments. This study investigated the effects of selenium and magnesium on hippocampal tissue in a mouse model of Pq-induced cognitive deficits. Thirty-five adult male mice weighing 15-28 g were divided into seven groups: Group A received normal saline at (0.5 mL/kg b.w), Group B (Pq-induced at 10 mg/kg b.w.), Groups C and D treated with selenium (0.3 mg/kg b.w) and magnesium (100 mg/kg b.w.) intraperitonially, and Groups E, F, and G (post-treated with selenium, magnesium, and both respectively after Pq exposure). Paraquat was administered daily for 3 weeks, while selenium and magnesium were administered intraperitoneally for 2 weeks. Hippocampal and hypothalamic tissues were analyzed histologically (Hematoxylin and Eosin), and orexin neurons were stained using immunohistochemistry. Markers of oxidative stress (glutathione GSH, superoxide dismutase SOD, catalase CAT, malondialdehyde MDA) were measured in brain tissue and blood serum. Cognitive function was assessed using the Morris water maze. Histological analysis revealed cellular changes in the Pq-treated and post-treatment groups (Pq+Mg, Pq+Se+Mg), whereas the other groups maintained intact morphology. Selenium treatment enhanced orexin neuron immunopositivity. The Pq-induced group exhibited elevated MDA levels and reduced SOD, CAT, and GSH levels in contrast with the control and post-treated groups. Selenium and magnesium treatments improved performance in the Morris water maze, with selenium significantly ameliorating oxidative damage. These findings suggest selenium and magnesium provide better protection against Pq-induced cognitive impairment than their combination.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
1. da Silva RA. Sleep disturbances and mild cognitive impairment: a review. Sleep sci. 2015; 8(1):36-41.
2. Olufunmilayo EO, Gerke-Duncan MB, Holsinger RD. Oxidative stress and antioxidants in neurodegenerative disorders. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(2):517.
3. Yadawa AK, Richa R, Chaturvedi CM. Herbicide Paraquat provokes the stress responses of HPA axis of laboratory mouse, Mus musculus. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2019; 153:106-115.
4. Yang X, Wang C, Zhang X, Chen S, Chen L, Lu S, Lu S, Yan X, Xiong K, Liu F, Yan J. Redox regulation in hydrogen sulfide action: From neurotoxicity to neuroprotection. Neurochem. Int. 2019; 128:58-69.
5. Chaabna N, Naili O, Ziane N, Bensouici C, Dahamna S, Harzallah D. In vitro Antioxidant, anti-Alzheimer and Antibacterial Activities of Ethyl acetate and n-Butanol Fractions of Punica granatum Peel from Algeria. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2023;7(7):3470-3477http://www.doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v7i7.27
6. Nixon JP, Mavanji V, Butterick TA, Billington CJ, Kotz CM, Teske JA. Sleep disorders, obesity, and aging: the role of orexin. Ageing res. rev. 2015; 20:63-73.
7. Scammell TE, Matheson JK, Honda M, Thannickal TC, Siegel JM. Coexistence of narcolepsy and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. aging. 2012; 33(7):1318-1319.
8. Fronczek R, van Geest S, Frölich M, Overeem S, Roelandse FW, Lammers GJ, Swaab DF. Hypocretin (orexin) loss in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. aging. 2012(8):1642-1650.
9. Mavanji V, Butterick TA, Duffy CM, Nixon JP, Billington CJ, Kotz CM. Orexin/hypocretin treatment restores hippocampal-dependent memory in orexin-deficient mice. Neurobiol. learn. mem. 2017; 146:21-30.
10. Ma Z, Jiang W, Zhang EE. Orexin signaling regulates both the hippocampal clock and the circadian oscillation of Alzheimer’s disease-risk genes. Sci. Rep. 2016; 6(1):36035.
11. Singh P, Sivanandam TM, Konar A, Thakur MK. Role of nutraceuticals in cognition during aging and related disorders. Neurochem. Int. 2021;143:104928.
12. Jáuregui-Lobera I. Iron deficiency and cognitive functions. Neuropsychiatr. dis. treat. 2014:2087-2095.
13. Cardoso BR, Roberts BR, Bush AI, Hare DJ. Selenium, selenoproteins and neurodegenerative diseases. Metallomics. 2015;(8):1213-1228.
14. Młyniec K, Davies CL, de Agüero Sánchez IG, Pytka K, Budziszewska B, Nowak G. Essential elements in depression and anxiety. Part I. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014;66(4):534-544.
15. Xu ZP, Li L, Bao J, Wang ZH, Zeng J, Liu EJ, Li XG, Huang RX, Gao D, Li MZ, Zhang Y. Magnesium protects cognitive functions and synaptic plasticity in streptozotocin-induced sporadic Alzheimer’s model. PloS one. 2014;9(9):e108645.
16. Prasad K, Tarasewicz E, Mathew J, Strickland PA, Buckley B, Richardson JR, Richfield EK. Toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics of paraquat accumulation in mouse brain. Exp. Neurol. 2009;215(2):358-367.
17. Atif F, Yousuf S, Agrawal SK. Restraint stress-induced oxidative damage and its amelioration with selenium. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008;600(1-3):59-63.
18. Yang Y, Yang J, Fan L, Wu D, Liu M, Yang Y. Immunohistochemical Staining Method for Neuropeptides in Mouse Brain. J Neurosci Methods. 2022;235:196-206.
19. Tsikas D, Suchy MT, Niemann J, Tossios P, Schneider Y, Rothmann S, Gutzki FM, Frölich JC, Stichtenoth DO. Glutathione promotes prostaglandin H synthase (cyclooxygenase)-dependent formation of malondialdehyde and 15(S)-8-iso-prostaglandin F2α. FEBS Lett.
2021;586(20):3723-3730.
20. Hadwan MH, Ali SK. New spectrophotometric assay for assessments of catalase activity in biological samples. Anal Biochem. 2018;542:29-33.
21. Sun Y, Yang J, Wang LZ, Sun LR, Dong Q. Determination of superoxide dismutase activity and its clinical applications. Biotech Histochem. 2020;95(7):536-547.
22. Bravo-Veyrat S, Hopfgartner G. High-throughput liquid chromatography differential mobility spectrometry mass spectrometry for bioanalysis: determination of reduced and oxidized form of glutathione in human blood. Anal. and bioanal. chem. 2018;410:7153-7161.
23. David AA, Oladele AA, Philip AO,Zabdiel AA, Olufunso AB, Tolulope OO, Adebola AO. Neuroprotective Effects of Garcinia kola ethanolic seed Extract on Haloperidol-Induced Catalepsy in Mice. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2022; 6(2):281-286.doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v6i2.18
24. Müller TE, Nunes ME, Menezes CC, Marins AT, Leitemperger J, Gressler AC, Carvalho FB, de Freitas CM, Quadros VA, Fachinetto R, Rosemberg DB. Sodium selenite prevents paraquat-induced neurotoxicity in zebrafish. Mol. Neurobil. 2018; 55:1928-1941.
25. Heredia L, Bellés M, Llovet MI, Domingo JL, Linares V. Neurobehavioral effects of concurrent exposure to cesium-137 and paraquat during neonatal development in mice. J. Toxicol. 2015; 329:73-79.
26. Baltazar MT, Dinis-Oliveira RJ, de Lourdes Bastos M, Tsatsakis AM, Duarte JA, Carvalho F. Pesticides exposure as etiological factors of Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases—a mechanistic approach. Toxicol. lett. 2014; 230(2):85-103.
27. Chen JG, Eldridge DL, Lodeserto FJ, Ming DY, Turner KM, Vanderford JL, Sporn TA, Schulman SR. Paraquat ingestion: a challenging diagnosis. J. Pediatr. 2010; 125(6)1505-1509.
28. Dardiotis E, Aloizou AM, Siokas V, Tsouris Z, Rikos D, Marogianni C, Aschner M, Kovatsi L, Bogdanos DP, Tsatsakis A. Paraoxonase-1 genetic polymorphisms in organophosphate metabolism. J. Toxicol. 2019; 411:24-31.
29. Kim J, Shin SD, Jeong S, Suh GJ, Kwak YH. Effect of prohibiting the use of Paraquat on pesticide-associated mortality. BMC public health. 2017; 17:1-1.
30. Jayasinghe SS, Seneviratne SA. Neurotoxic effects of paraquat. Galle Med. J. 2016; 21(2).
31. Dalwadi DA, Ozuna L, Harvey BH, Viljoen M, Schetz JA. Adverse neuropsychiatric events and recreational use of efavirenz and other HIV-1 antiretroviral drugs. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018; 70(3):684-711.
32. Opii WO, Sultana R, Abdul HM, Ansari MA, Nath A, Butterfield DA. Oxidative stress and toxicity induced by the nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)—2′, 3′-dideoxycytidine (ddC): relevance to HIV-dementia. Exp. Neurol. 2007; 204(1):29-38.
33. Case AJ, Agraz D, Ahmad IM, Zimmerman MC. Low‐Dose Aronia melanocarpa Concentrate Attenuates Paraquat‐Induced Neurotoxicity. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016; 2016(1):5296271.
34. Aaseth J, Alexander J, Bjørklund G, Hestad K, Dusek P, Roos PM, Alehagen U. Treatment strategies in Alzheimer’s disease: a review with focus on selenium supplementation. Biometals. 2016; 29:827-839.
35. Solovyev ND. Importance of selenium and selenoprotein for brain function: From antioxidant protection to neuronal signaling. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015; 153:1-2.
36. Gröber U, Schmidt J, Kisters K. Magnesium in prevention and therapy. Nutrients. 2015; 7(9):8199-8226.
37. Stelmashook EV, Isaev NK, Zorov DB. Paraquat potentiates glutamate toxicity in immature cultures of cerebellar granule neurons. Toxicol. Lett. 2007;174(1-3):82-88