Anti-diabetic Effect of Ethyl acetate Extract of Spondias mombin (Linn) Stem Bark in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
Main Article Content
Abstract
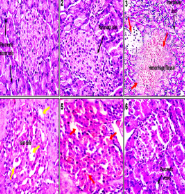
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to insulin deficiency or resistance. Spondias mombin (Linn), commonly known as hog plum, is a tropical plant traditionally used for various medicinal purposes. This research aimed to assess the impact of ethylacetate extract from the stem bark of Spondias mombin (ESM) on blood glucose and various biochemical parameters in rats with diabetes induced by streptozotocin (STZ). STZ-induced diabetic rats were categorized into six groups, each comprising five rats (n = 5). The first group served as the healthy control; the second group included healthy rats given 100 mg/kg of ESM, while groups 3 to 6 contained STZ-induced rats treated with 0.6 mL/kg of water, 50 mg/kg of metformin, 50 mg/kg of ESM, and 100 mg/kg of ESM respectively over a 14-day period. Weekly blood glucose levels were measured using test strips and an Accu-Chek glucometer. Biochemical assessments, including lipid profile, liver function, and kidney function tests, were conducted following standard procedures. Histological examination of the rats’ pancreas was performed after the experimental duration. The daily oral administration of ESM at doses of 50 and 100 mg/kg body weight in STZ-induced diabetic rats revealed a restoration of glucostasis, along with improvements in kidney, liver, and lipid dysfunction associated with diabetes. The extract positively influenced the pathological alterations in the pancreas caused by diabetes induction. S. mombin stem bark exhibits a glucose-lowering effect and ameliorates the pathological complications linked to diabetes.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
IDF diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of undiagnosed diabetes in adults for 2021
Ribeiro C, De-Alencar CS, Voltarelli FA, De-Araújo MB, Botezelli JD. Effects of Moderate Intensity Physical Training in Neonatal Alloxan-Administered Rats. J Diab Metab. 2010; 1:107.
Uppu RM, Parinandi NL. Insulin Sensitization and Resistance Interrelationship Revisited with a Quantitative Molecular Model Approach. J Diabetes Metab. 2011; 2:106e.
Da-Silva SB, Costa JP, Pintado ME, Ferreira DC, Sarmento B. Antioxidants in the Prevention and Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy - A Review. J Diabetes Metab. 2010; 1:111.
Kowluru RA, Chan PS. Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Retinopathy. Exp Diabetes Res. 2007; 7(1): 43603.
Vishwarkarma SL, Sonawane RD, Rajani M, Goyal RK. Evaluation of effect of aqueous extract of Enicostemma littorale Blume in streptozotocin induced type 1 diabetic rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 2010; 48: 26-30.
Sani D, Sanni S, Nguide SI. Phytochemical and antimicrobial screening of the stem aqueous extract of Anisopus manni. J Med Plant Res. 2009; 3(3): 112-115.
Martinez MJA, Lazaro RB, Olmo LMBD, Benito PB. Anti-infectious activity in the anthemideae tribe. Stud Nat Prod Chem. 2008; 35: 445-516.
Olugbuyiro JA, Moody JO, Hamann MT. Phytosterols from Spondias mombin Linn. with anti-mycobacterial activities. Afr J Biomed Res. 2013; 16: 182-186.
Adepoju OT, Oyewole OE. Nutrient Composition and Acceptability Study of Fortified Jams from Spondias Mombin (Hog Plum, Iyeye in Yoruba) Fruit Pulp. Nig J Nut Sci. 2008; 29: 180-189.
Nworu CS, Akah PA, Okoli CO, Okoye TC. Oxytocic activity of leaf extract of Spondias mombin. Pharm Biol. 2007;45: 366- 371
Osuntokun OT, Ige OO, Idowu TO, Cristina GM. Bio-activity and Spectral Analysis of Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectroscopy (GC-MS) Profile of Crude Spomdias mombin Extracts. SF J Anal Biochem. 2018; 2: 1-12.
Lorenzi H, Matos FJA. Medicinal plants of Brazil: Native and exotic. Instituto Plantarum, Nova Odessa. 2008; 32-40
Fred-Jaiyesimia A, Kio A, Richard W. Amylase inhibitory effect of 3 - olean-12-en-3-yl (9Z)-hexadec-9-enoate isolated from Spondias mombin leaf. Food Chem. 2009;116: 285-288
Silva ARA, Morais SM, Marques MMM, Lima DM, Santos SCC, Almeida RR, Vieira IGP, Guedes MIF. Antiviral activities of extracts and phenolic components of two Spondias species against dengue virus. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2011;17: 406-413
Abo KA, Ogunleye VO, Ashidi JS. Antimicrobial potential of Spondias mombin, Croton zambesicus and Zygotritonia crocea. Phytother Res. 1999;13: 494-497
Gobinath RM, Parasuraman S, Sreeramanan S, Enuguth B, Chinni SV. Antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic effects of methanolic extract of leaves of Spomdias mombin in STZ-induced diabetes rats. Front. Physiol. 2022;13: 1-11
Fred-Jaiyesimi A, Abo K. Anti-diabetic Activity of Spondias mombin Extract in NIDDM Rats. Pharm Biol. 2009;47(3): 215-218. DOI: 10.1080/13880200802462493
Omoboyowa DA, Agoi MD, Shodehinde SA, Saibu OA, Saliu JA. Anti-diabetes study of Spondias mombin (Linn) stem bark fractions in high-sucrose diet-induced diabetes in Drosophila melanogaster. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2023;18(4): 663e675
Omoboyowa DA, Karigidi KO, Aribigbola TC. Nephro-protective efficacy of Blighia sapida stem bark ether fractions on experimentally induced diabetes nephropathy. Comp Clin Pathol. 2021;30: 25–33 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-020-03186-w
Kassirer JP. Clinical evaluation of kidney function--glomerular function. N Engl J Med. 1971;285(7): 385-9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197108122850706.
Tanganelli E, Prencipe L, Bassi D, Cambiaghi S, Murador E. Enzymic assay of creatinine in serum and urine with creatinine iminohydrolase and glutamate dehydrogenase. Clin. Chem. 1982;28(7): 1461-1464
Thefeld W, Hoffmeister H, Bush EN, Koller PU, Vollinar J. Reference values for the determination of GOT, GPT and alkaline phosphatase in serum with optimal standard methods. Dtsch Med. Wochenschr. 1974; 99(8): 343-344
Walter M, Gerard H. Ultra-micro method for the determination of conjugated and total bilirubin in serum or plasma. Micro chem J. 1980;15: 231–236
Allain CC, Poon LS, Chan CS, Richmond W, Fu PC. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1974;20(4): 470-475
Jacobs NJ, VanDemark PJ. The purification and properties of the alpha- glycerophosphate oxidizing enzyme of Streptococcus faecalis. Arc Biochem Biophys. 1960;88: 250-255
Assmann G. Current diagnosis of hyperlipidemias. Internist (Berl). 1979;20(11): 559-564
Avwioro OG. Histochemistry and tissue pathology, principle and techniques. Claverianum press, Nigeria 2010; Pp: 23-26
Lenzen S. The mechanisms of alloxan- and streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia. 2007; 51: 216-226.
Guo Y, Jiang N, Zhang L, Yin M. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Fritillaria cirrhosa and its anti-diabetic activity on Streptozotocin induced rats. Arab J Chem. 2020; 13(4): 5096-5106.
Prasad S, Gupta SC, Aggarwal BB. Serendipity in Cancer Drug Discovery: Rational or Coincidence? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2016;37(6): 435-450
Coskun O, Kanter M, Korkmaz A, Oter S. Quercetin, a flavonoid antioxidant, prevents and protects streptozotocin-induced oxidative stress and β-cell damage in rat pancreas, Pharmacol. Res. 2005; 51: 117-123.
Ghasemi A, Sajad JKK. The Laboratory Rat: Age and Body Weight Matter. EXCLI J. 2005:1431-1445.
Ogur R, Coskun O, Korkmaz A, Oter S, Yaren H, Hasde M. High nitrate intake impair sliver functions and morphology in rats; protective effects of α-tocopherol. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2005; 20(1): 161–166.
Gheibi S, Jeddi S, Carlström M, Gholami H, Ghasemi A. Effects of long-term nitrate supplementation on carbohydrate metabolism, lipid profiles, oxidative stress, and inflammation in male obese type 2 diabetic rats. Nitric Oxide. 2018;75: 27–41
Keyhanmanesh R, Hamidian G, Alipour MR, Ranjbar M, Oghbaei H. Protective effects of sodium nitrate against testicular apoptosis and spermatogenesis impairments in streptozotocin-induced diabetic male rats. Life Sci. 2018; 211: 63–73.
Oghbaei H, Alipour MR, Hamidian G, Ahmadi M, Ghorbanzadeh V, Keyhanmanesh R. Two months sodium nitrate supplementation alleviates testicular injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetic male rats. Exp Physiol. 2018; 103(12): 1603–1617.
Gundala NK, Naidu VG, Das UN. Amelioration of streptozotocin-induced type-2 diabetes mellitus in Wistar rats by arachidonic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018; 496(1): 105-113.
Adams DM, Yakubu MT. Aqueous extract of Digitaria exilis ameliorates diabetes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic male Wistar rats. J Ethnopharmacol, 2019; 11: 23-83. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2019.112383
Latifi E, Mohammadpour AA, Fathi B, Nourani H. Antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic effects of ethanolic Ferulaassa-foetida oleo-gum-resin extract in streptozotocin-induced diabetic wistar rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019; 110: 197-202.
Mondal A, Bhar R, Sinha SN. Ethnomedicinal value and Biological Activities of Spondias mombin L-A Concise Review. Asian Res J Cur Sci. 2021;87-94.
Eluehike N, Onoagbe I. Changes in organ and body weight, serum amylase and antidiabetic effects of tannins from Spondias mombin on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Insul Resist. 2018;3(1): 1-5.
Hu X, Cheng D, Zhang Z. Anti-diabetic activity of Helicteres angustifolia root. Pharm Biol. 2016;54: 938-944.
Gad-Elkareem MAM, Abdelgadir EH, Badawy OM, Kadir A. Potential anti-diabetic effect of ethnaolic and aqueous-ethanolic extracts of Ricinus communis leaves on streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Peer J. 2019;7: 6441.
Mehta AR. Why does the plasma urea concentration increase in acute dehydration? Adv. Physiol Educ. 2008;32: 336.
Han J, Pang X, Zhang Y, Peng Z, Shi X, Xing Y. Hirudin protects against kidney damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy rats by inhibiting inflammation via P38/MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14: 3223.
Kalaiselvi A, Reddy GA, Ramalingam V. Ameliorating effect of ginger extract (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) on liver marker enzymes, lipid profile in aluminum chloride induced male rats. Int J Pharm Sci Drug Res. 2015;7: 52-58.
Dong L, Yu L, Liu A, Alahmadi TA, Almoallim HS, Durairaj K. Ononin mitigates streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats via alleviating oxidative stress and inflammatory markers. J King Saud Univ-Sci. 2022;102029.
Annadurai T, Muralidharan AR, Joseph T, Hsu MJ, Thomas PA, Geraldine P. Antihyperglycemic and antioxidant effects of a flavanone, naringenin, in streptozotocin–nicotinamide-induced experimental diabetic rats. J Biochem Physiol. 2012;68(3): 307-318
Genç F, Peker EGG. Does Short-Term and Low-Dose N-Acetylcysteine Affect Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in The Liver Tissues of Diabetic Rats? Biol Res Nursing. 2021; 23(4): 568-574. doi:10.1177/10998004211003668
Joshi D, Mittal DK, Shukla S, Srivastav AK, Srivastav SK. N-acetyl cysteine and selenium protects mercuric chloride-induced oxidative stress and antioxidant defense systemin liver and kidney of rats: a histopathological approach. J of Trace Elem in Med and Biol. 2014;28: 218-226.
Bhowmik B, Siddiquee T, Mujumder A, Afsana F, Ahmed T, Mdala IA, Moreira NC, Khan AKA, Hussain A, Holmboe-Ottesen G, Omsland TK. Serum Lipid Profile and Its Association with Diabetes and Prediabetes in a Rural Bangladeshi Population. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15(9):1944. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15091944.
Kumar S, Kumar V, Prakash OM. Antidiabetic and hypolipidemic activities of Kigelia pinnata flowers extract in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012;2(7): 543-546
Maruthupandian A, Mohan VR. Anti-diabetic, anti-hyperlipidaemic and antioxidant activity of Pterocarpus marsupium Roxb. In alloxan induced diabetic rats. Int J Pharm Tech Res. 2011;3(3): 1681-1687.